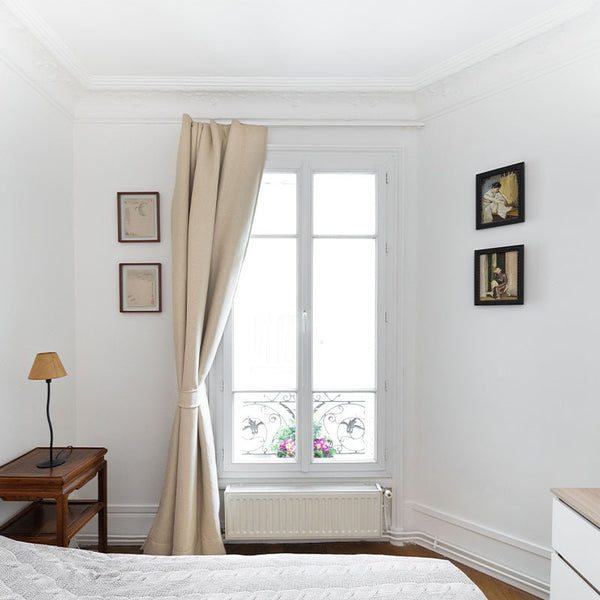
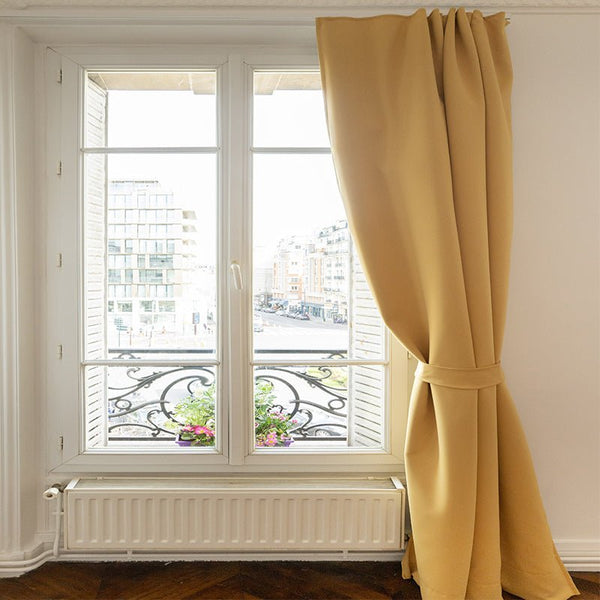
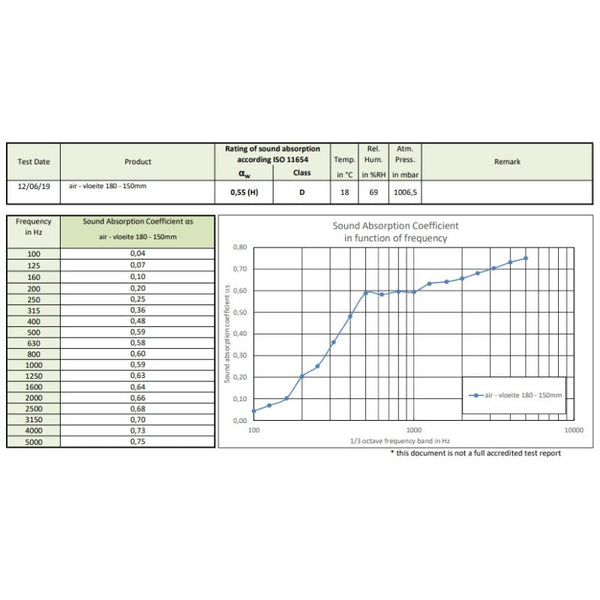
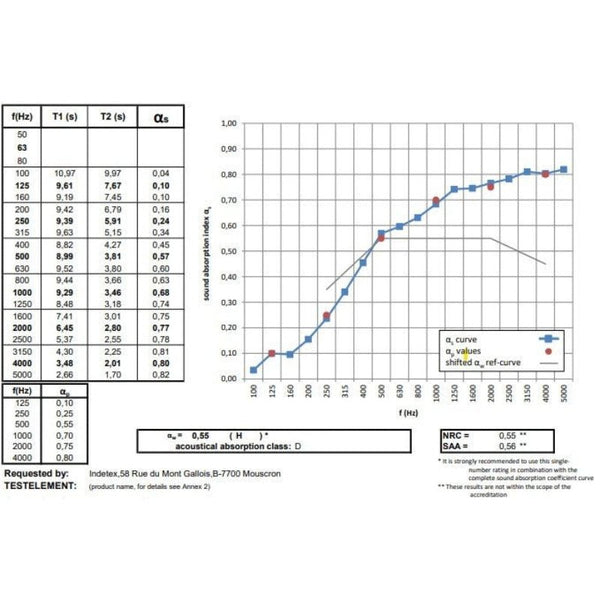
We all know how important it is to keep our home comfortable, especially in winter. Good thermal insulation with anti-cold curtains plays a crucial role in this. The aim of this article is to show you the importance of calculating the thermal insulation coefficient, and to guide you through the process of improving your home's energy efficiency. Properly insulating your home is a long-term investment that will benefit you in terms of comfort and energy savings. Heat loss in the home can account for up to 30% of total energy costs. So a precise understanding of how thermal insulation coefficients work and how to calculate them is a major asset for any homeowner looking to make substantial savings.
The importance of thermal insulation
Thermal insulation is essential for maintaining a stable temperature inside your home, regardless of the weather conditions outside. It helps you save energy, reduce your heating bills and make a positive contribution to the environment. Not only does good thermal insulation keep the heat in, it also reduces cold draughts and damp, preventing problems such as mold and condensation.
The importance of understanding and calculating thermal insulation coefficients
Knowing how to calculate the thermal insulation coefficient, also known as the U-value, is crucial. This value indicates the performance of an insulating material. The lower the U-value, the better the insulation. A good grasp of this concept enables you to choose the right materials and combine the most effective solutions for maximum optimization. For example, knowing that glass wool has a low thermal conductivity means you can make informed decisions for your insulation work. In this article, we'd like to provide you with a practical guide to better insulating your home using thermal curtains. You'll learn how these curtains can improve your home comfort, as well as various strategies for optimizing their use. You'll be able to compare different materials and choose the ones that offer the best performance for your specific needs. We'll also present case studies and practical tips for maximizing the effectiveness of your home's thermal insulation.
Understanding the thermal insulation coefficient
Definition of thermal insulation coefficient (U-value)
The U-value measures the amount of heat that passes through a material per unit area and temperature difference. It is expressed in watts per square meter-kelvin (W/m²-K). This coefficient enables us to better understand how a material behaves in the face of heat exchange, and therefore to better choose your materials for optimum insulation. In practice, the U-value is essential in determining the efficiency of various construction elements such as walls, floors and windows. For example, a window with a U-value of 1 W/m²-K is much more efficient than one with a U-value of 3 W/m²-K. This information is crucial for renovation projects, where improving insulation not only increases comfort, but also saves money on energy bills.
Importance of U-value in the context of energy efficiency
A low U-value means that the material is a good insulator, helping to keep heat inside your home in winter and maintain coolness in summer. This value is one of the main indicators of the quality of your insulation. As a result, it has a direct impact on your energy bills and the thermal comfort of your home. The thermal regulation achieved by a low U-value also helps reduce heating and air-conditioning use, which has a positive impact on the environment. By choosing materials with a low U-value for your insulation, you help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and preserve natural resources.
How does U-value affect the performance of thermal curtains?
Thermal curtains with a low U-value will prevent heat escaping through windows, increasing your home's energy efficiency. These curtains are designed to provide an extra barrier against heat loss, which is particularly useful in older homes where windows are not always well insulated. Thermal curtains can also be used to complement other insulation systems such as roller shutters or insulating window film. When used together, these tools optimize insulation and further improve your home's energy efficiency, reducing the need to overheat or overcool your living space.
Thermal curtain materials and properties
Description of materials commonly used in thermal curtains
The most common materials used in thermal curtains include wool, polyester and fleece linings. Each of these materials has unique insulating properties. Wool, for example, is known for its excellent insulating qualities thanks to its fibrous structure, which traps air and reduces thermal conduction. Polyester, on the other hand, is a synthetic material that offers good insulation while being lightweight and easy to maintain. By choosing the right material for your thermal curtains, you can optimize their efficiency and maximize energy savings. For example, wool curtains will be more suitable for cold climates, while polyester curtains may be more effective in temperate regions where keeping cool is a priority.
Comparing the insulating properties of different materials
Wool is an excellent insulator thanks to its low thermal conductivity. Polyester, on the other hand, is more affordable and just as effective when combined with specific linings. Wool curtains also offer superior durability, making them particularly suitable for intensive use. What's more, wool's ability to regulate humidity contributes to enhanced interior comfort. On the other hand, polyester is often preferred for its ease of maintenance and lower cost. By combining this material with insulating fleece linings, you can achieve thermal performance comparable to that of wool, while benefiting from a lower initial cost. The key is to understand the specifics of each material and choose the one that best suits your needs and budget.
Impact of different fabrics and linings on thermal insulation
Linings, such as fleece, significantly increase the effectiveness of thermal curtains by adding an extra layer of insulation. Multiple layers of fabric can also be used to enhance insulation, with each additional layer increasing overall thermal resistance. For example, a thermal curtain combining a polyester outer layer with a fleece lining offers superior thermal insulation to a single polyester curtain. What's more, some thermal curtains include reflective barriers that reflect heat back into the room, increasing their energy efficiency. By understanding these factors, you can make informed choices that maximize the insulating effect of your thermal curtains.
Methodology for calculating thermal insulation coefficients
Steps for calculating the thermal insulation coefficient
Introduction to formulas and units of measurement
To calculate the U-value, use the following formula: U = 1 / R where R is the thermal resistance of the material (in m²-K/W). This formula determines a material's ability to resist the passage of heat. The higher the R, the better the insulation. Thermal resistance, in turn, depends on the thickness of the material and its thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity (lambda) is a measure of a material's ability to transfer heat. It is expressed in W/m. By combining this information with the thickness of the material, you can determine the thermal resistance, which gives you a precise idea of the insulation's efficiency. This calculation method is universal and applies to all types of insulating material.
Step-by-step guide to calculations
- determine the thickness of the insulation (in meters). For example, a thermal curtain may be 0.01 meters thick;
- measure the material's thermal conductivity (lambda) (in W/m-K). Ask yourself questions such as: Where does the material come from? What is its capacity to conduct heat?
- Calculate thermal resistance using the formula R = thickness / lambda. For example, for a material with a thermal conductivity of 0.04 W/m-K and a thickness of 0.01 meter, you would find R = 0.01 / 0.04 = 0.25 m²-K/W ;
- calculate the U-value using the formula U = 1 / Using our example, this would give U = 1 / 0.25 = 4 W/m²-K.
This allows you to compare different materials and configurations to identify those that offer the best insulation for your home. In practice, you can use these calculations to evaluate the performance of various thermal curtains and select those that maximize your home's energy efficiency.
Practical examples to illustrate the calculation
For a curtain with a thickness of 0.01 metre and a material with a thermal conductivity of 0.04 W/m-K, the thermal resistance would be 0.01 / 0.04 = 0.25 m²-K/. So the U-value would be 1 / 0.25 = 4 W/m²-. This allows you to compare different materials and choose those that offer the best combination of cost and performance. For example, you may find that a wool curtain offers better insulation than a polyester curtain, despite a higher initial cost. These calculations also enable you to understand the impact of material thickness on insulating efficiency. By slightly increasing the thickness of the curtain, you can significantly improve its thermal resistance, and therefore reduce the value. As a result, even minor adjustments can have a significant impact on overall insulation performance.
Use of calculation tools and resources
Tools and resources for calculating thermal insulation coefficients
There are a number of online tools and software packages like Recticel, Vmc and Dp that can help you quickly calculate the thermal insulation coefficient. These tools automate calculations and deliver accurate results in just a few clicks. They are often equipped with material databases, making it easy to compare different insulation options. Other resources include regulatory guides and standards such as NF EN ISO 6946, which specifies calculation methods for the thermal resistance and U-value of building elements. These guides are essential to ensure that your calculations comply with industry standards and that the solutions you choose are optimized for energy performance. Using these tools and resources, you can run simulations to assess the impact of different material configurations and insulation techniques. This enables you to make informed decisions and choose the solutions that will deliver the best performance for your home.
Optimize thermal insulation with thermal curtains
Tips for improving home insulation
Remember to install good quality thermal curtains, and even consider using additional linings. Make sure your curtains fit snugly and cover the windows completely. Thermal curtains should be long enough to touch the floor and wide enough to cover the entire window. This helps minimize heat loss through the gaps and sides of the curtains. You can also use accessories such as thermal curtain rods and clips to improve the efficiency of your curtains. Spring rods help keep curtains tightly closed against window sills, reducing draughts. Also, remember to screw windows back together or install seals to eliminate incoming draughts.
Examples of thermal curtain configurations for different window types
For standard windows, use adjustable curtain tracks and rodsto maximize efficiency. For larger windows, thicker thermal curtains with multi-layer linings are recommended. In addition, you can use roller blinds combined with thermal curtains for extra insulation. For roof windows, thermal curtains with special fasteners are required to ensure hermetic closure. There are also specific solutions for corner windows and conservatories, where bespoke thermal curtains can be installed to maximize insulation. By adapting your insulation solutions to the specific features of each window, you can optimize your home's energy performance.
Case studies and testimonials
Studies have shown that the use of thermal curtains canreduce heat loss through windows by up to 25%. Many users report significant reductions in their heating bills. For example, in a detached house in a cold region, the installation of thermal curtains reduced heating consumption by an average of 15% over one year. Another case study involved a house in an urban area where the installation of thermal curtains not only improved insulation, but also reduced external noise pollution. Occupants reported a significant improvement in acoustic comfort, in addition to the thermal benefits. These testimonials demonstrate the effectiveness of thermal curtains not only for thermal insulation, but also for the general well-being of occupants.
Nokomis, your expert for successful insulation
Accurately calculating the thermal insulation coefficient is crucial for an energy-efficient home. For high-quality thermal curtains, explore the range on the Nokomis website. We offer solutions tailored to every type of home to maximize your comfort and energy efficiency. Our experts can help you choose the best products based on your specific needs and budget constraints. Don't hesitate to inquire about the financial assistance available for insulation work. In France, programs such as the CITE (Tax Credit for Energy Transition) and subsidies from the